What is a Passive Infrared Sensor? Working, Uses & Benefits Explained
- Kalyan Bhattacharjee

- Jul 29, 2025
- 2 min read
Updated: Aug 1, 2025
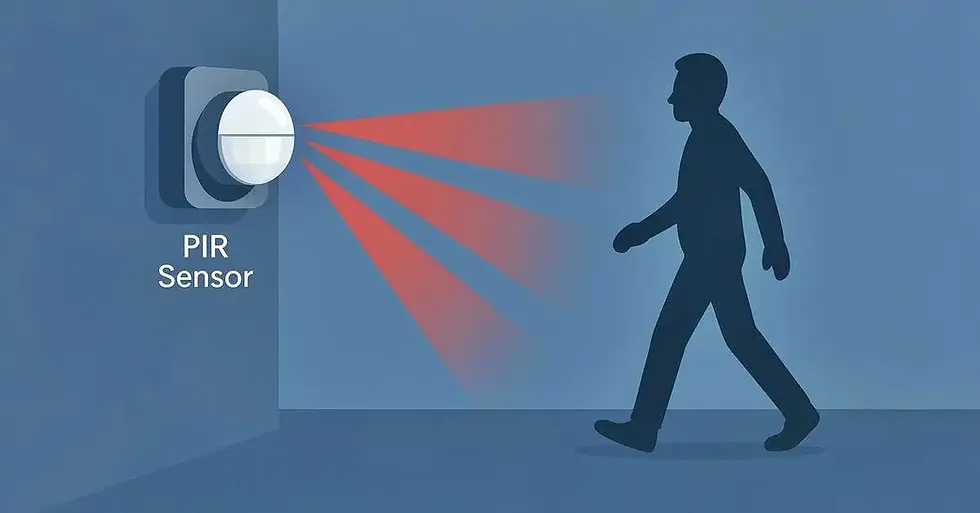
Ever wondered how lights turn on by themselves? That’s the magic of PIR sensors.
TL;DR
Passive Infrared (PIR) sensors detect motion by measuring changes in infrared (IR) radiation emitted by objects. They are commonly used in home security, automation systems, and lighting controls. PIR sensors are cost-effective, energy-efficient, and only detect living beings that emit heat, like humans and animals.
What is a Passive Infrared (PIR) Sensor?
A Passive Infrared sensor, or PIR sensor, is an electronic device that detects infrared (IR) radiation emitted by objects in its field of view. Unlike active sensors, PIR sensors do not emit any energy themselves they are passive - and instead measure IR radiation naturally emitted by warm bodies, such as humans or animals.
How PIR Sensors Work
PIR sensors have two main components:
Pyroelectric sensor: This detects IR radiation and converts it into an electrical signal.
Fresnel lens or mirror: Focuses the IR radiation onto the sensor.
When a warm object moves across the sensor’s detection zone, the change in IR levels is detected, triggering a response. For example, turning on a light or sending an alert.
Real-World Applications of PIR Sensors
PIR sensors are widely used in:
Home security systems: Motion-detecting alarms and CCTV cameras.
Automatic lighting: Turning lights on/off in rooms, staircases, or hallways.
Smart devices: Used in smart fans, AC systems, and other automated electronics.
Energy conservation: Reduces power usage by activating systems only when needed.
Advantages of PIR Sensors
✅ Low Power Consumption
✅ Affordable and Widely Available
✅ No Need for Line-of-Sight
✅ Only Triggers for Living Beings (No False Alarms from Static Objects)
✅ Works Well in Indoor Environments
Limitations of PIR Sensors
❌ Limited Range: Usually effective within 5–10 meters
❌ Can’t Detect Through Walls or Glass
❌ Affected by Ambient Temperature Changes
❌ Slower Response for Very Slow Movements
Important Tips for Using PIR Sensors
Mount Height Matters: Install 6–8 feet high for best coverage.
Avoid Heat Sources: Don’t place near radiators or direct sunlight.
Motion Direction Matters: Movement across the sensor is detected more easily than movement directly toward it.
Regular Cleaning: Dust or grime can interfere with IR detection.

Wrapping Up
PIR sensors are simple, efficient, and incredibly useful for a wide range of motion-detection applications. Their passive design, combined with low power usage and high reliability, makes them a go-to choice for both home and commercial automation.
✍️ Written by Kalyan Bhattacharjee
Digital Creator | AI Visionary | Fintech Shield
passive infrared sensor, passive infrared motion sensor, passive infrared pir motion sensor, passive infrared sensor vs motion detector, passive infrared sensors, what is passive infrared sensor, how does passive infrared sensor work, how passive infrared sensors work, pir sensor meaning, pir sensor, passive ir motion sensor, pir motion sensor how it works, pir detector, PIR sensor working principle, what is a PIR sensor, pir motion detector, passive infrared technology, fintech shield




Comments